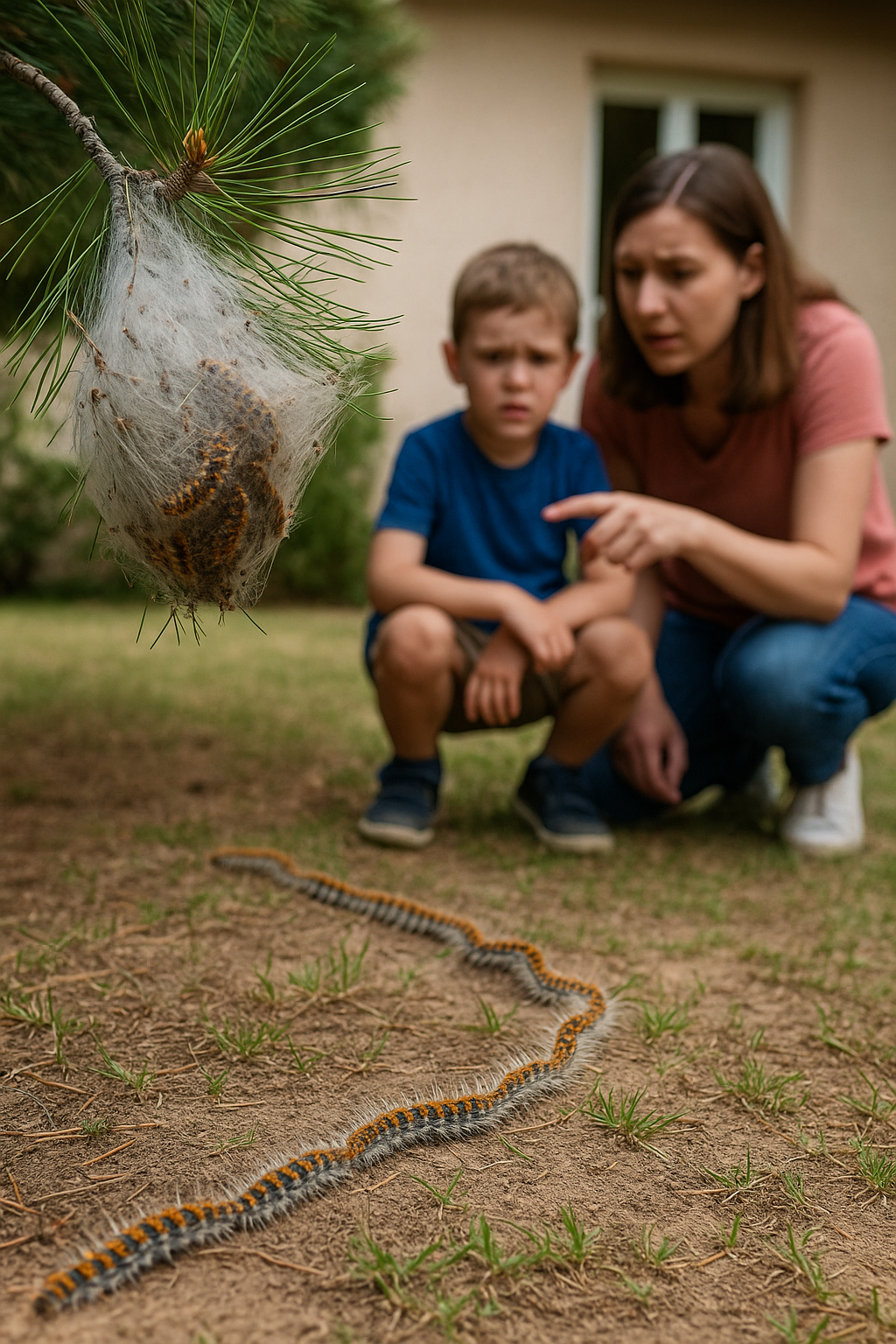
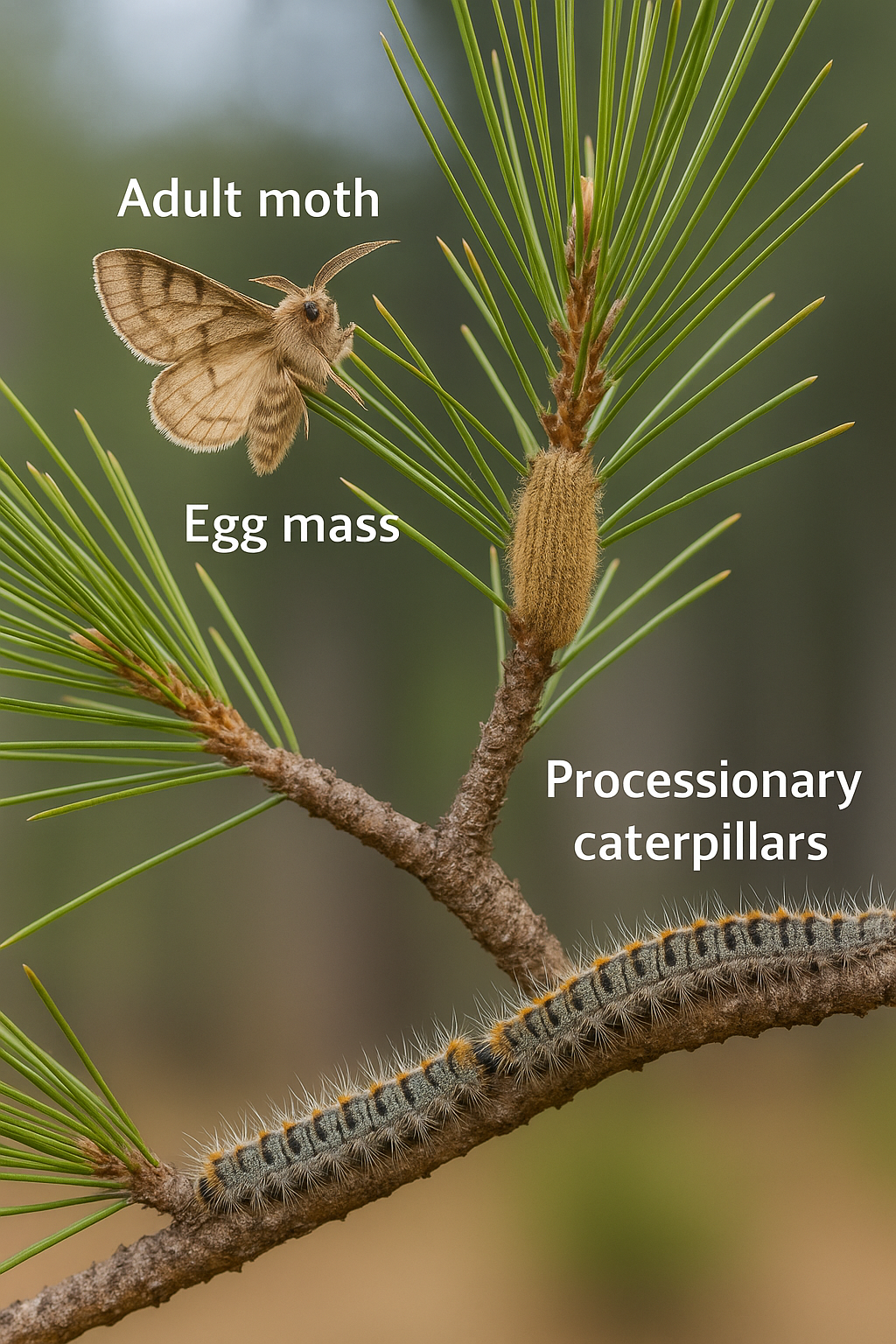
The pine processionary moth (Thaumetopoea pityocampa) poses a real risk to human health, especially in areas near pine trees and gardens. Its stinging hairs are easily shed and can cause serious reactions in both children and adults.
How stinging hairs work
Adult caterpillars release very fine hairs (setae) that contain stinging toxins and proteins, such as thaumetopoein. These hairs can be raised in the air and deposited on the skin, mucous membranes or breathed in. ([Wikipedia, Thaumetopoein](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thaumetopoein))
These hairs have microscopic hooks that easily dig into the skin and release irritating substances.
Risks and symptoms in children and adults
- Urticarial dermatitis and skin rashes: red reactions, intense itching and papules. :contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
- Eye irritation: conjunctivitis, itching, swelling, even hairs embedded in the cornea. :contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}
- Respiratory symptoms: cough, difficulty breathing, asthma or asthma attack in allergic cases. :contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2}
- Systemic allergic reactions: anaphylaxis, facial edema, allergic shock in severe cases. :contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3}
- Mucous and respiratory orifices: the hairs can affect the nose, throat or even the bronchi. :contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}
Possible medical conditions
Below are some documented examples of disorders caused by the processionary moth:
- Contact dermatitis: immediate or delayed after contact with caterpillar hairs. :contentReference[oaicite:5]{index=5}
- Asthma or allergic bronchitis: by inhalation of hairs. :contentReference[oaicite:6]{index=6}
- Orofacial or periorbital edema in children: documented cases of facial swelling after contact. :contentReference[oaicite:7]{index=7}
- Anemia or allergic shock: in hypersensitive people, there may be a severe systemic reaction. :contentReference[oaicite:8]{index=8}
Risk factors and sensitivity
- People with a history of allergies or asthma will be at higher risk.
- Prolonged or repeated exposure may sensitize and increase the severity of reactions. :contentReference[oaicite:9]{index=9}
- Areas close to infested trees increase the risk of hairy air. :contentReference[oaicite:10]{index=10}
Prevention and action in the garden
- Avoid having pine trees very close to children's play areas.
- Remove processionary nests or bags before the caterpillars grow.
- Keep the garden clean, avoid dead leaves and debris that scatter hairs.
- Wear clothing that covers the skin (long-sleeved shirts, gloves).
- In case of contact: wash with water and neutral soap, avoid rubbing, see a doctor if there is an intense reaction.
Outstanding scientific references
- Skin Reactions to Pine Processionary Caterpillar (PMC)
- Skin Reactions on Exposure to the Pine Processionary
- Allergy to pine processionary caterpillar (Thaumetopoea)
- An unusual case of processionary moth reaction
- Occupational Exposure of Forest Workers to Urticating Setae
- Non-occupational allergy caused by the pine processionary
It is essential not to underestimate the risks: if you have pine trees near your garden, taking control measures with professionals can prevent serious health problems.